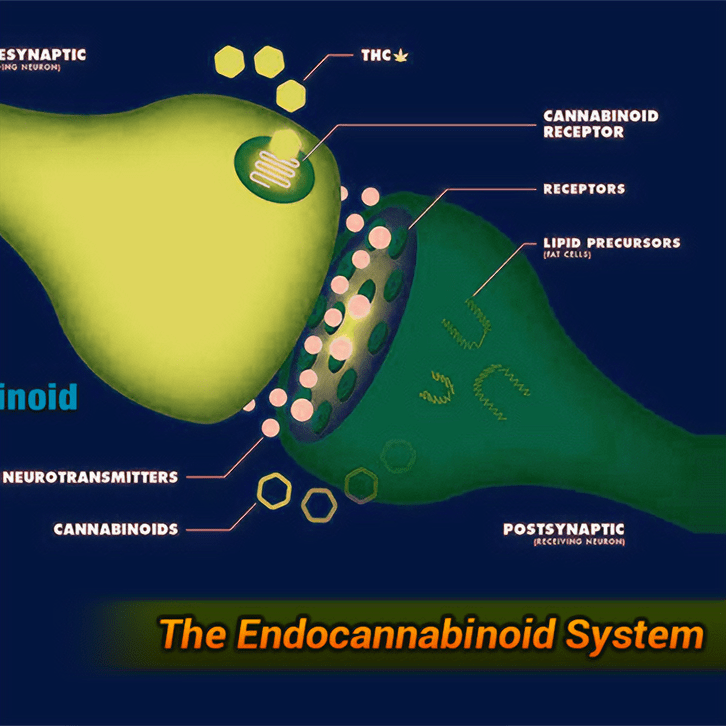
If you are new to the world of cannabis and its healing ways, then you may be wondering exactly how it all works. This is a topic that can get very in depth, so we will focus on a term you may have heard, cannabinoids. The human endocannabinoid system and cannabinoids are the key components to how all of this works!
What are cannabinoids?
You may have heard the term cannabinoid, but what exactly is it? Cannabinoids are chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant that act with receptors in our bodies to help maintain health and stability. There are two main types of cannabinoids: phytocannabinoids, which are produced by plants, and endocannabinoids, which are produced internally by our own bodies (more on this later).
There are nine major phytocannabinoids, but scientists have discovered more than eighty-five that plants produce. The nine major phytocannabinoids are: THC, CBD, THCA, CBDA, CBN, CBGA, CBG, CBC, and THCV. The two we hear about most are THC and CBD. THC (which stands for tetrahydrocannabinol) is most known for its psychoactive effects, but is also helpful for managing pain, reducing inflammation, nausea and vomiting, as a sleep aid, and more. CBD (cannabidiol) is only recently becoming a more popularly used cannabinoid, and it is useful for treating epilepsy, cancer, anxiety, inflammation and more. There are countless health issues that can be positively affected by these cannabinoids.
What is the endocannabinoid system?
As is true of most people, you may never have heard of the endocannabinoid system because it was only discovered in 1992 by Israeli researchers. The endocannabinoid system, or ECS, is a network of cell receptors positioned throughout our bodies that is responsible for helping regulate many aspects of our health from emotional wellbeing to the physical functioning of muscles, nerves and brain tissue.
These receptors bind with our endocannabinoids to complete a neurotransmission process that helps keep our body healthy and in balance. Our ECS is responsible for helping regulate our mood, appetite, memory, pain, inflammation, muscles, nerves, brain tissue, bone growth, and much more!
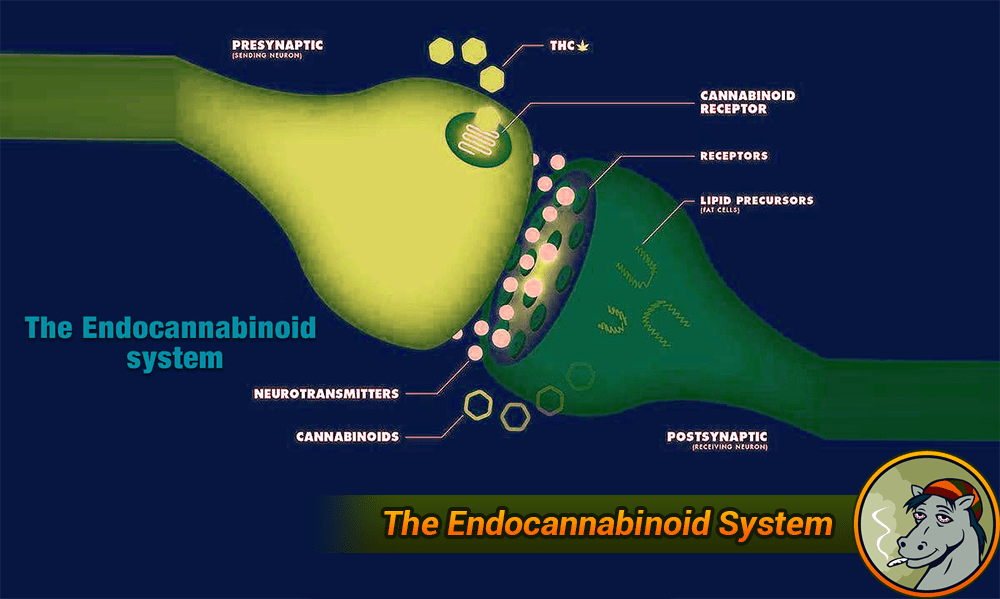
How do they interact with each other?
Our ECS receptors are both directly and indirectly affected by the various cannabinoids. When reacting with receptors, cannabinoids can be agonists as well as antagonists, meaning they can either activate or deactivate certain ECS receptors throughout the body. Our bodies and ECS are constantly changing. When the system is not functioning properly it is the cannabinoids job to help balance everything out. The type and amount of each cannabinoid determines which parts of the system are affected.
As you can see the world of cannabis healing is truly complex. There are countless components that when interacting create varying effects on our bodies. Depending on your symptoms and metabolism, there are cannabinoids and doses of each that can give you the healing effects you desire. It is amazing that internal endocannabinoids (and external phytocannabinoids applied through cannabis medicine) affect so many different parts of our bodies and the symptoms we have. It is also highly likely that some combination of them is exactly the help that you need!
References:
- Knox, Jessica. “Your Beginner’s Guide to the 9 Major Cannabinoids.” Green Flower Media, 18 July 2018, www.green-flower.com/articles/128/beginners-guide-to-cannabinoids.
- Frye, Gregory. “9 Essential Questions about Your Body’s Endocannabinoid System.” Green Flower Media, 20 Mar. 2019, www.green-flower.com/articles/421/9-questions-about-your-body-s-endocannabinoid-system.